
Tip closest to residents to remain untouched
May 8th 2025
This information seeks to clarify which tips are included in ERI Ltd’s proposal to mine and then flatten certain coal tips in Caerphilly. The tips selected appear to be on the basis of which would be most profitable to mine of the ‘waste coal’ they contain…

The Bill that risks reigniting coal mining in Wales
May 6th 2025
The Welsh Government’s Deputy First Minister, in his response to the CCEIC’s Stage 1 Report, admits the “Bill does not prevent the extraction or burning of coal” but adds “I cannot envisage a scenario in which the extraction and burning of coal will arise as a result of the Bill”…

Coal in industry
April 25th 2025
The direct use of coal as a feedstock (not just energy) is particularly significant in China, where coal is used extensively in coal to gasification plants to produce chemicals such as methanol, ammonia, and…

The natural world of Glan Lash
April 18th 2025
This nature was photographed around 50 metres from the edge of the Glan Lash opencast coal mine in Ammanford, South Wales. It shows the thriving ecosystems surrounding the Glan Lash opencast coal mine which has remained dormant since 2019…

Committee takes forward CAN’s key recommendations
April 15th 2025
In February, CAN gave oral testimony to the Climate Change, Energy, and Infrastructure Committee (CCEIC) on the Disused Mine and Quarry Tips (Wales) Bill…

Westminster: our evidence on Wales’ coal legacy
April 7th 2025
Coal Action Network was invited to attend Westminster where we gave evidence to the Welsh Affairs Committee in their inquiry about the environmental and economic legacy of Wales’ industrial past, alongside Friends of the Earth Cymru. This inquiry was opened in…

Lethal landscape: cuts to Ffos-y-fran mine restoration puts community at risk
March 25th 2025
16 years of opencast coal mining in Ffos-y-fran has generated colossal overburden mounds, also known as slag heaps or coal tips. There are three coal tips, with the third being the largest, and cumulatively accounting for 37 million cubic metres of colliery spoil, rocks, and soil…

We’re back in the Senedd giving oral evidence
March 24th 2025
We were invited for the second time to give oral evidence to the Climate Change, Environment, and Infrastructure Committee of the Welsh Parliament (Senedd) on 05th February 2025. We shared the panel with Haf, Director of FOE Cymru, to provide our opinion on the weaknesses, strengths…
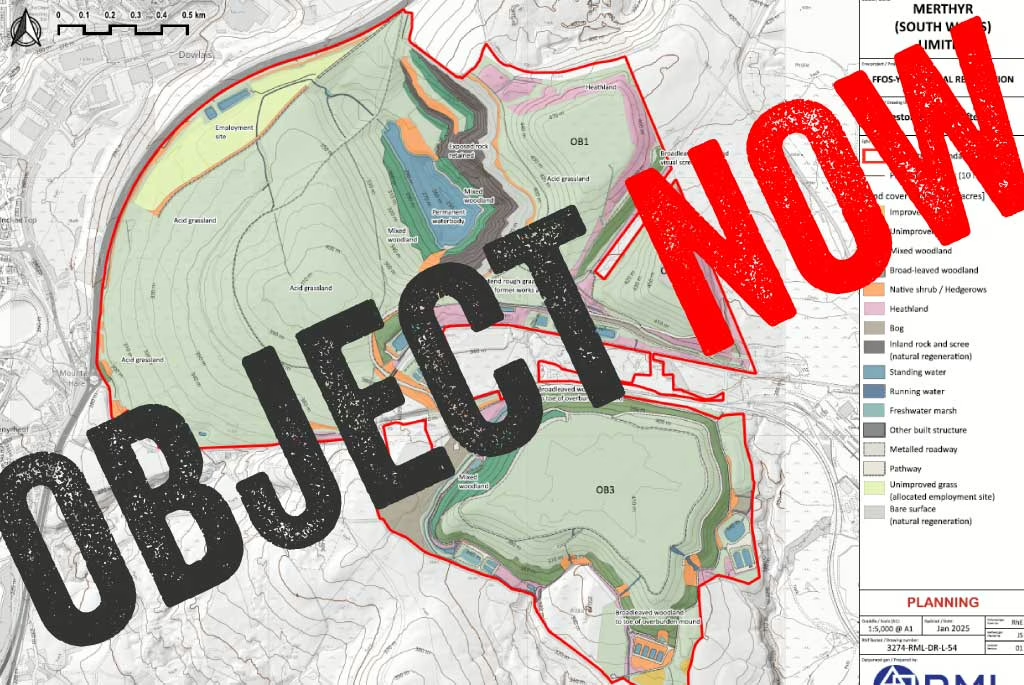
Demand nature be restored to Ffos-y-fran opencast site
February 28th 2025
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…