Concerned you don't have all the details to talk to people on the street about the proposed West Cumbria coal mine? This page gives suggestion answers to some of the more detailed questions campaigners get asked about West Cumbria Mining Ltd's plans for Whitehaven. Have a look and see if they help you feel more confident speaking about this campaign.
They serve as guide answers, you may have your own.

West Cumbria Mining Ltd want to mine 2.78 million tonnes of coal a year until 2049. The company aims to produce around 64 million tonnes of coal in total, from a predominantly undersea mine.
This would result in 0.34 million tonnes of methane being released during the process of mining, and a further 200 million tonnes of CO2 when the coal is burned. The methane would account for almost 40% to the UK’s fossil production methane emissions by 2030, putting critical methane targets at risk. The CO2 is equivalent to the United Arab Emirates' total 2021 emissions.
"We need the coal for power stations"
The coal is destined for foreign steelworks, it’s not the type normally used in power stations. The UK got less than 2% of its energy from coal last year, we don’t need more coal to keep lights on.
"We need the coal for UK steel making"
Almost all the coal would be exported. Both the UK’s major steelworks – at Port Talbot and Scunthorpe – have confirmed they will close their coal-based blast furnaces and install electric arc furnaces which recycle scrap steel without coal. At present this scrap steel is exported to be recycled abroad and then recycled steel is reimported. There is plenty of scope to increase UK-based recycling.
 "The coal would be high quality"
"The coal would be high quality"
Coal from Whitehaven is high in sulphur and causes acid rain when burnt. So its use is restricted by the UK and European Union. This means the coal is most likely to be sold to Turkey, outside the EU – a major steelmaker with lower pollution standards.
In order to reduce the sulphur content of the coal, it would need to be either blended with low sulphur coal, like that mined in Australia, or it would need to be ‘ barrel washed’. There’s no information from West Cumbria Mining Ltd on how washing would be done, or where the polluted waste from washing would go.
"You can’t make steel without coal"
The main way that new steel is made currently uses coal, but already 9% of steel is made by Direct Reduction which doesn’t need to use coal. Direct Reduction can use hydrogen (or fossil fuels, inc. coal). Only hydrogen made from renewables can be considered green.
In the UK there are already 4 steelworks that recycle scrap steel in electric arc furnaces and 2 major steelworks with blast furnaces which use large amounts of coal. The latter are the UK’s 2nd and 3rd biggest single site emitters of CO2. The blast furnace operators have agreed to convert to electric arc furnaces and stop using coal within the next few years, with one expected to convert in March 2024.
The UK government has been investing in carbon capture and storage projects, which have been unsuccessful in capturing significant quantities of greenhouse gasses. The UK is behind other European countries on investment in new green steel technology. There are new primary steel manufacturing methods that use green hydrogen with direct reduction iron that can be utilised in the UK if there was political will.
"You still need coal in electric arc furnaces (EAF)"
Although the lobby group UK Steel says 9kg of coking coal may be used in EAF to produce a tonne of steel (versus 780kg for a tonne of blast furnace steel), other sources of carbon are possible to completely exclude coal use, using the same infrastructure.
"You can’t always use recycled steel"
In the construction industry, steel is often over-supplied by as much as 50%. We can use far less to build the same amount of things. We need to employ engineers to more accurately calculate what is needed, and reduce the amount of raw materials produced.
Steel must be part of the circular economy, alongside reducing use and reusing it before recycling, rather than extracting more materials to make ever more goods.
Companies like Volvo, and top-end manufacturers like Porche, are demanding green steel for their cars. Advances in technology mean ever more metal is able to be recycled and progress in design can reduce contaminants in scrap metal.
 "It would be a carbon-neutral mine"
"It would be a carbon-neutral mine"
Coal mines are not carbon-neutral. They release methane, a powerful greenhouse gas whilst coal is being mined and release CO2 when the coal is later burned.
Once coal is brought above ground it will be burnt, as companies can make a profit. So coal mined in West Cumbria would worsen climate change through increased coal use. Mining coal in Cumbria doesn't mean it will be left underground somewhere else, as companies with planning permission will sell everything they can having already invested in mines.
The International Panel on Climate Change says that we cannot be net-zero by 2050 if we open any more fossil fuel extraction sites and that we have to close some of the existing ones.
Gold Standard is the carbon offsetting company that West Cumbria Mining Ltd intended to pay to offset emissions from its proposed coal mine by planting trees or supporting renewable schemes. However, Gold Standard responded to this intention by saying “Our claims guidelines make it clear that to make an offset claim organisations should prioritise the avoidance and reduction of emissions – something that is clearly impossible for a coalmine”. Even if an offsetting company wanted this business, the coal mine’s methane emissions would not be offset.
"The methane will be captured"
West Cumbria Mining Ltd doesn’t intend to begin collecting methane released from the proposed coal mine until 5 years after the project starts. The majority of this highly potent greenhouse gas is released when the mine is first created, so even if methane capture equipment caught and burnt 100% of methane released (which it won’t) it will be too little, too late.
"We need the jobs"
Whitehaven may need more jobs but the jobs in this mine, were it to go ahead, would be very different to those in previous local mines. The project would be technologically advanced and employ far fewer people that mines traditionally. Most likely the company would bring in foreign workers, such as Australian miners experienced with ultra-modern mines.
Unionised green jobs can be created in Whitehaven with the right government support, such as for trades people insulating the poor quality housing stock, or improving public transport and doing good for the area as well as creating work. A Just Transition for Cumbria is crucial and means that the community is put at the heart of decisions and workers are leading their industries.
"People from out of the area can’t tell us what to do"
People living in Whitehaven are also concerned about the ecological and climate impacts that this mine would have. If the mine goes ahead, the coal will worsen climate change which affects us all. No-one in Cumbria wants to be flooded by increasingly heavy rains washing away soil in fields and devastating homes, nor to experience droughts brought on by extreme temperatures. Climate change will bring both.
"It’s a local mining company"
West Cumbria Mining Ltd is 81% owned by EMR Capital, a private equity investment fund that manages various mines, with offices in Australia, the Cayman Islands tax haven, and Singapore. The head of EMR Capital used to work for the infamous Rio Tinto. The investors in the project are predominantly from Australia and the USA. There are no local offices or employees of WCM Ltd.
 "Mining is our heritage"
"Mining is our heritage"
We can be proud of our mining heritage and still want a different future.
Our world has changed since coal mining brought stable work and the community of the pits. We no longer need to risk people’s lives in mining coal seems that we know to be gassy and dangerous—we have other ways to make steel and to heat homes.
"Contamination in proposed area"
The Marchon Bank Chemical works was closed in 2005. It had been a detergent factory, as well as the largest single-site producer of sulphuric acid in Europe and the largest single-site producer of Sodium Tripolyphospate in the world. There were also phosphoric acid plants.
The land was registered as contaminated. Although nothing changed at the site, the status was removed in 2013 when the site was approved for a biomass plantation and public access.
If mining were to go ahead, it would involve removing large concrete pads locking in the contamination at the site, this presents a risk of airbourne toxins. This is a risk, especially to the people living in the hundreds of new houses built around the northern and eastern perimeters of the site.
"They only want to dump nuclear waste"
The company that is behind West Cumbria Mining Ltd, EMR Capital, is a holdings company which buys global mining projects (not just for coal) and extracts minerals. If all the permissions and contracts are in place and the project is financially viable then coal mining will happen here.
It may be possible that once the site stops being economically viable or is sold to another company, that nuclear waste from Sellafield or further afield could be dumped in the dug out areas. We can’t assume that the only reason they want permission to mine is to dump nuclear waste, the opportunity to extract coal and turn a profit is too big to be ignored for nuclear waste dumping alone.
"There’s nothing that can be done to stop it"
There is not a coal mine on this site. There is still everything to play for.
To operate the project likely needs a license for the undersea section from the Marine Management Organisation – which could take a year to get from the time of application. There are other permissions and there has to be companies – including investors and insurance companies - prepared to aid a new coal mine in the 2020s. A new government could stop the application or the current legal challenge against its permission may force a new decision.
There’s lots we can still do. The last underground coal mine to be permitted in the UK, New Crofton Co-operative Colliery, never started.

"A coal mine needs insurance"
Coal mines have to obtain insurance to operate. If there is no insurance then there is no coal mine.
Financial firms and big investors won’t put money into a project which doesn’t have insurance to ensure that their investments are protected.
Campaigning to stop the insurance of fossil fuels keeps them in the ground
More details
 We've designed cards that you can print at home with short summaries of these answers in case you'd feel happier talking to people about the proposed mine with a reminder with you. Download here.
We've designed cards that you can print at home with short summaries of these answers in case you'd feel happier talking to people about the proposed mine with a reminder with you. Download here.
Good luck

Coal Action Network is proud to present our 2026 manifesto for Wales. With the Senedd elections taking place in May this year, Wales stands at a decisive moment. For over a century, coal has shaped Welsh landscapes, communities, and politics. Today, Wales has the opportunity to shape something very different…

As part of our Politics Unspun series we are unpacking politicians’ public comments on coal to challenge any misleading or incorrect messages. Todays’ focus is on comments made during a Westminster Hall debate in December 2025 about the oil refining sector. During the debate, Lee Anderson MP made some statements about coal…

The Government is reforming planning policy in England and thanks to thousands of our supporters asking for an end to coal extraction in the last consultation in 2024, they are now recommending that planners “should not identify new sites or extensions to existing sites for peat or coal extraction”…
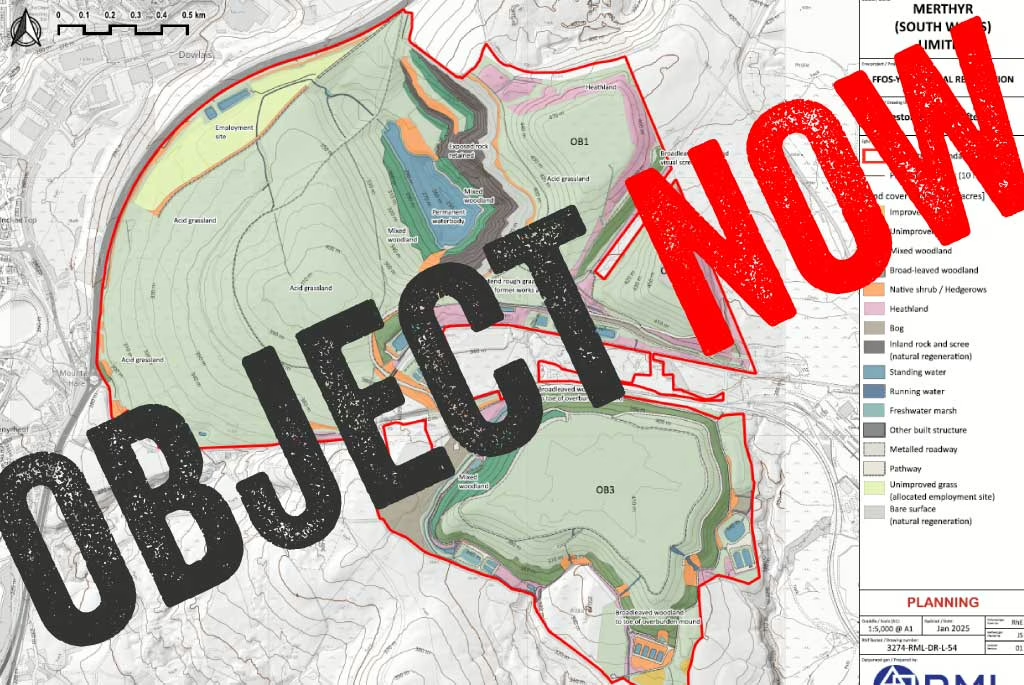
Merthyr (South Wales) Ltd mined for over a year illegally after planning permission for the Ffos-y-fran opencast coal mine ended in September 2022. During that year, it made record-breaking profits due to sanctions on Russia and other factors driving up the price of coal. But rather than using some of the profits from that ill-gotten coal…

In November 2024, the new UK Government announced its intention to legislate a ban of new coal mining licences – which we welcomed. Over a year later, the legislation is yet to be introduced, and the Government is not planning to include all types of extraction…

The UK steel and cement sectors (and to a lesser extent, bricks) are the largest users of coal following the closing down of the UK’s last coal-fired power station in September 2024. Check out our coal dashboard for our most recent coal stats including an industry break-down. We support the UK Government’s commitment to ban…

The steel industry produces 9-11% of the annual CO2 emitted globally, contributing significantly to climate change. In 2024, on average, every tonne of steel produced led to the emission of 2.2 tonnes of CO2e (scope 1, 2, and 3). Globally in 2024, 1,886 million tonnes (Mt) of steel were produced, emitting…

Last month we worked with Members of Parliament from various parties on a Westminster Hall debate about coal tip safety and the prohibition of new coal extraction licences. The debate happened 59 years and one day after the Aberfan tragedy which killed 116 children and 28 adults…

Successful, at-scale, examples already exist of cement works burning 100% fuel alternatives to traditional fossil fuels, including pilot projects using combinations of hydrogen and biomass (UK) and hydrogen and electricity (Sweden). Yet, innovations such as use of hydrogen and kiln electrification are…